Assessment of the medial compartment is step 4 of diagnostic arthroscopy. Biomechanical evaluation of orthoses shows that there are potentially beneficial biomechanical changes to joint loading;
The perpendicular distance between the ground reaction force vector and the knee’s center of rotation (moment arm) produces an external adduction moment (also called varus moment), which has been identified as the mechanism primarily responsible for much of the compressive load on the medial compartment.
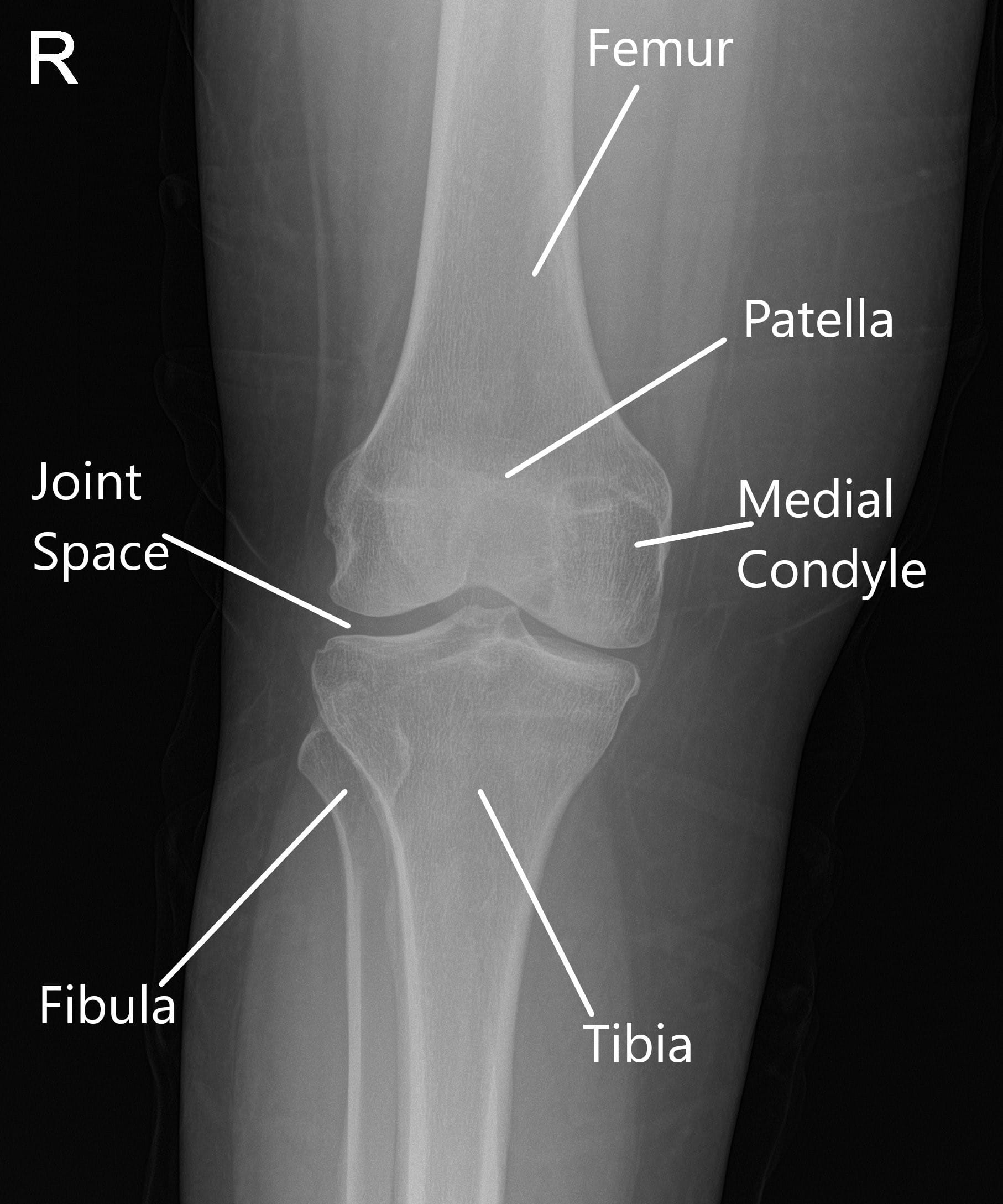
Medial compartment of knee. Lateral compartment, located on the outer side of the knee. Osteoarthritis is the most common type of knee arthritis that can be affected by excessive and compressive loads and can affect one or more compartments of the knee: Between the two bones is the joint space.
The three compartments that make up the knee are the: Medial compartment, near the middle of the knee, on the inner side In particular, primary knee oa often presents with a varus malalignment.
The knee itself is made up of three compartments: The mcl is located on the inside (medial side) of the knee, connecting the inside, bottom edge of the femur with the inside, top edge of the tibia. These attachments connect to the top of the tibia/shin bone and/or the end of the femur/thigh bone.
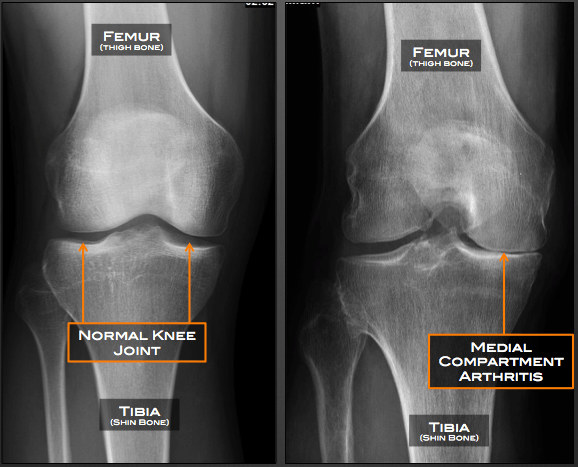
Outward (varus) force across the knee. The mcl helps to stabilize the knee by limiting inward (valgus) force across the knee. Knee osteoarthritis (oa), the most common type of chronic arthritis disease characterized by degeneration and loss of articular cartilage, regeneration in subchondral bone, osteophyte formation, and synovial inflammation [], affects almost 250 million people worldwide and leads to severely physical dysfunction [].medial compartment knee oa is the most.
An arthroscopic probe rests on top of the medial meniscus. Medial compartment, located near the middle of the knee on the inner side. • the medial collateral ligament (mcl).
In a further related study [26] sasaki and yasuda did examine the subjective pain reports experienced by 40 persons with medial compartment knee osteaorthritis who received This increases the loads going through the medial compartment resulting in. The inside of your knee, also called the medial knee or the medial compartment, is the area of the knee that�s closest to your opposite knee.
The knee is divided into three major compartments: The lateral compartment is on the other side of your knee. 47,53,76 the larger adduction (varus) moment shifts the.
The medial femoral condyle (a) and medial tibial plateau (c) are assessed for chondromalacia, and the medial. The medial compartment tends to be the most vulnerable to injuries and research suggests that a better understanding of the medial to lateral. When osteoarthritis starts, it usually does so in one of the three compartments in the knee.
The perpendicular distance between the ground reaction force vector and the knee’s center of rotation (moment arm) produces an external adduction moment (also called varus moment), which has been identified as the mechanism primarily responsible for much of the compressive load on the medial compartment. Introduction knee osteoarthritis (oa) is a disease common in older adults that can result in significant disability The medial/inside compartment of the knee includes muscle, tendon, ligament, and medial meniscus, or “cartilage” attachments.
Arthroscopic view of the medial compartment of a right knee from the anterolateral portal. Chondroplasty may be separately reported when performed in a separate compartment of the same knee as the meniscus repair. These attachments connect to the top of the tibia/shin bone and/or the end of the femur/thigh bone.
Deterioration of this cushion layer, also known as cartilage, results in your knee bones rubbing together. Lateral compartment, on the outer side of the knee; The medial ligament complex of the knee is composed of the superficial medial collateral ligament, deep medial collateral ligament, and the posterior oblique ligament.
Medial compartment knee osteoarthritis, noting satisfactory subjective reports of pain relief when applied to individuals with symptomatic osteoarthritic varus knees. Over time, this leads to knee pain, knee joint stiffness and swelling [source: Medial compartment osteoarthritis involves the knee joint, whereby the cushioning layer between your knee bones deteriorates over time.
Knee osteoarthritis (oa) is the most common joint disorder worldwide. The medial/inside compartment of the knee includes muscle, tendon, ligament, and medial meniscus, or “cartilage” attachments. Assessment of the medial compartment is step 4 of diagnostic arthroscopy.
Medial knee injuries are the most common type of knee injury. The onset of medial compartment osteoarthritis, as well as other forms of knee arthritis, typically begins in middle or older age [source: Medial compartment osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage of the knee deteriorates.
In addition to pain, other common. Medial knee pain typically occurs because of a deterioration of cartilage. Most frequently, the treatment of choice would be a total knee replacement, which involves removing healthy joint surfaces in such patients.
The medial compartment is the side of your knee closest to the other knee. Medial compartment (the inside part of the knee) lateral compartment (the outside part of the knee) patellofemoral compartment (the front of the knee between the kneecap and thighbone) However, evaluation in relation to clinical outcome measures in.
Patellofemoral compartment, formed by the kneecap and part of the femur. Also to know is, what are the medial and lateral compartments of the knee? The medial, or inner compartment is the most common area for arthritis to start.
The presence of excessive medial joint laxity in individuals with medial compartment knee oa may delay or inhibit neuromuscular responses because greater joint excursions are required to activate high threshold mechanoreceptors. The results of conservative treatment of knee osteoarthritis (oa) are generally evaluated in epidemiological studies with clinical outcome measures as primary outcomes. Biomechanical evaluation of orthoses shows that there are potentially beneficial biomechanical changes to joint loading;
Cpt® code 29883 reports a meniscus repair in both the medial and lateral compartments, while cpt® code 29882 reports a meniscus repair in either the medial or lateral compartment. Thus, when an unexpected perturbation occurs, the unprepared neuromuscular system may be incapable of appropriately activating the correct.