Recent drug intake, infections, lymphoproliferative disorders, and connective tissue disorders should be ruled out before labeling a patient as primary itp. You can ask questions (and get answers) about treatments (medical and.
A better understanding of the underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms and associated predictive markers would help differentiate subgroups of patients with itp and personalize treatment.
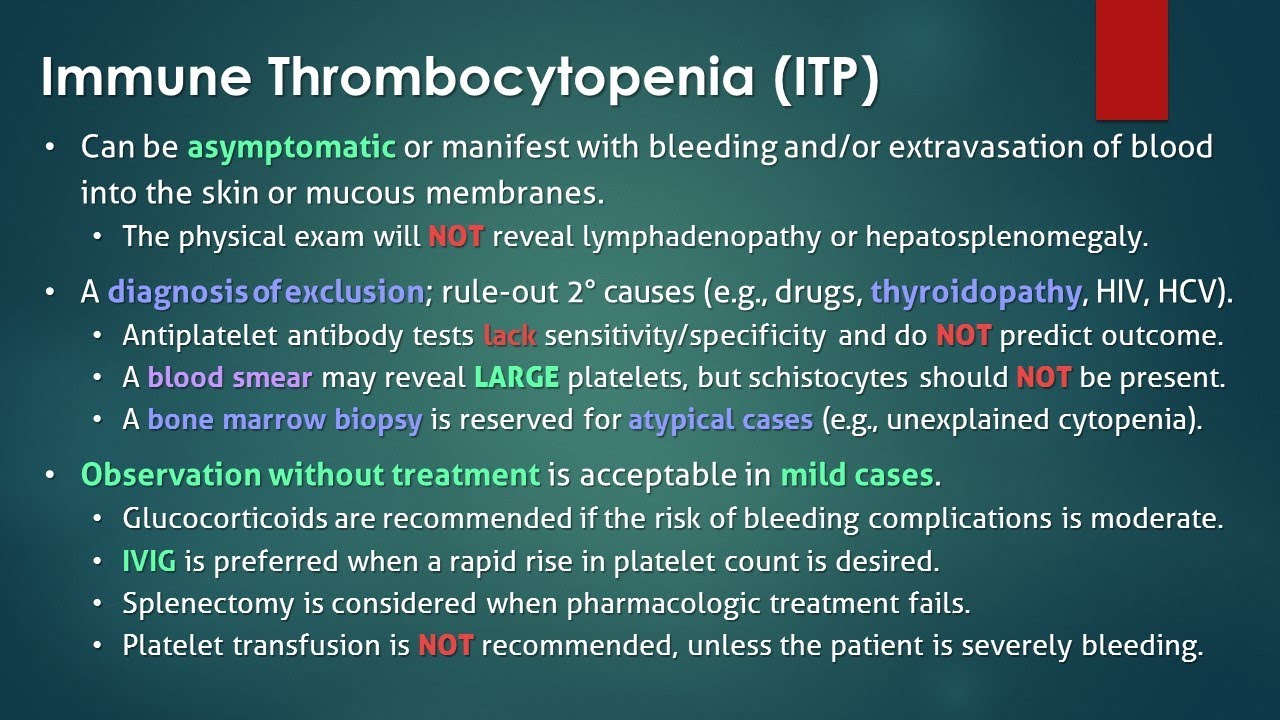
Itp diagnosis and treatment. No specific tests exist to confirm the diagnosis. This test provides the count of each type of blood cell, including red blood cells (rbcs), white blood cells (wbcs), and platelets. We reviewed the literature using google scholar, pubmed and clinicaltrial.gov databases as.
14 a recent randomized clinical trial documented that a combination of four days of dexamethasone plus four weekly infusions of rituximab resulted in sustained safe platelet counts over 50×10 9 /l at six. Itp can usually be identified by: Complete blood count (cbc), including a hematologist’s examination of the blood under the microscope.
Treatment includes corticosteroids, splenectomy, immunosuppressants, thrombopoietin receptor agonist drugs, or the spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor fostamatinib. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura is a condition consisting of a decreased platelet count. Recent drug intake, infections, lymphoproliferative disorders, and connective tissue disorders should be ruled out before labeling a patient as primary itp.
You can ask questions (and get answers) about treatments (medical and. Because the diagnosis of itp is one of exclusion and clinical suspicion, a test that could help us definitively identify the diagnosis would be useful. Response to treatment is the only affirmative confirmation of diagnosis.
Itp is diagnosed by identifying a low platelet count on a complete blood count (a common blood test). Complete blood count (cbc) : This review summarizes a comprehensive update on the diagnostic and therapeutic modalities for itp.
Sometimes treatment is not necessary. Response to treatment is the only affirmative confirmation of diagnosis. Itp can be diagnosed in children with a physical exam and medical history analysis.
Diagnostic procedures for itp other diagnostic procedures include: [] an advantage of iv rhig is that if bone marrow aspiration is unacceptable to parents and if the diagnosis of acute itp is equivocal, iv rhig is an effective. However, since the diagnosis depends on the exclusion of other causes of a low platelet count, additional investigations (such as a bone marrow.
Your doctor will likely suggest these treatments for itp first: Adults who have itp with very low platelet counts or bleeding problems often are treated. Recently rituximab has become an alternative second treatment for patients with itp, although the rate and durability of responses appear to be less than with splenectomy.
The normal platelet count for a. Itp is a diagnosis of exclusion; This facebook group has 7.7 thousand members and averages about 170 new posts a month.
Thus, no confirmation of diagnosis exists. Your medical provider may also suggest the following tests : Diagnosing itp is the first step in managing this autoimmune disorder.
Dexamethasone or prednisone is typically prescribed to raise your platelet count. In cases where the platelet count is very low or there is evidence of bleeding, some form of treatment should be started. Measures the size, number and maturity of different blood cells in a specific volume of blood (to measure platelets).
No specific tests exist to confirm the diagnosis. A diagnosis of exclusion, based on patient history, physical examination, complete blood count and examination of the peripheral blood smear, is used for. Diagnosis of itp in children.
In some cases, itp goes away by itself. Treatment for itp includes time and close observation. Initial treatment of patients with newly diagnosed itp includes observation, a corticosteroid, and/or ivig depending on platelet count and bleeding symptoms.
But the term idiopathic was abandoned because it literally means “of an unknown cause”, and the cause is now known to be. Itp is a diagnosis of exclusion; Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is a blood disorder characterized by an abnormal decrease in the number of platelets in the blood.
Itp is a diagnosis of exclusion; When treatment is necessary, the two main treatment options are steroids and intravenous gamma globulin. The first section of this review carefully evaluates the diagnostic considerations in patients with.
Treatment for immune thrombocytopenia (itp) is based on how much and how often you�re bleeding and your platelet count. The first step in treating your child is forming an accurate and complete diagnosis. Regarding the name, it has changed several times in the past few decades.
Learn more about itp diagnosis at stanford. Learn more about diagnosis and treatment options, such as medication or surgery. No specific tests exist to confirm the diagnosis.
A decrease in platelets can result in easy bruising, bleeding gums, and internal bleeding. Itp may be acute and resolve in less than 6 months, or chronic and last longer than 6 months. Diagnosis is usually clinical, based on exclusion of other reversible causes of thrombocytopenia (eg, hiv and hepatitis c infections).
This practice point applies to children aged 90 days through 17 years who have typical, newly diagnosed primary immune thrombocytopenia (itp). We monitor the condition closely to see if the disorder corrects on its own. Patients classified as refractory have a diagnosis that is not really itp or have disease that is difficult to manage.
Adults who have mild itp may not need any treatment, other than watching their symptoms and platelet counts. Find out more about our approach to itp treatment. A better understanding of the underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms and associated predictive markers would help differentiate subgroups of patients with itp and personalize treatment.
Response to treatment is the only affirmative confirmation of diagnosis. In the past, it was known as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Primary immune thrombocytopenia (itp) is an autoimmune disease characterized by increased destruction and impaired production of platelets caused by autoantibodies directed against the platelets and megakaryocytes and an increased risk of bleeding.the incidence in adults has been estimated between 1.6 and 3.95 x 100 000 subjects per year, depending on the.
