
This helps stop a clot from getting bigger and keep new clots from forming. A pulmonary embolism (pe) is when a blood clot becomes stuck in the blood vessels of your lung.
This helps stop a clot from getting bigger and keep new clots from forming.
How to treat pulmonary embolism. Also described as blood thinners, these medicines decrease the ability of the blood to clot. Wible b.c., buckley j.r., cho k.h. Heparin is a regularly used anticoagulant for pulmonary embolism (pe) which can be given via the vein or instilled beneath the skin.
How is a pulmonary embolism treated? Surgery to remove the embolus from the pulmonary artery. Treatment is aimed at keeping the blood clot from getting bigger and preventing new clots from forming.
Figure 1 anticoagulant agents and dosing: The main treatment for pulmonary embolism is called an anticoagulant. A pulmonary embolism is often caused by the formation of a deep vein thrombosis (dvt) which then breaks free and travels to the lung, causing a blockage within the pulmonary artery.
Blood thinners or anticoagulants are the most common treatment for a blood clot in the lung. For the first 10 days after the pulmonary embolus has occurred, treatment consists of one of the following anticoagulant drugs:. An interventional procedure in which a filter is placed inside the body’s largest vein (vena cava filter) so clots can be trapped before they enter the lungs.
Treatment choices for pulmonary embolism (pe) include: Take all medicines as prescribed, and have blood tests done as. The current established regimen for management of pulmonary embolism is illustrated in figure 2.
Examples include warfarin and heparin. Drugs called anticoagulants are the first tools doctors reach for if you’ve had a pulmonary embolism. But the good news is that if it’s caught early, doctors can treat it.
Bleeding risk associated with thrombolysis. It is seldom fatal when diagnosed and treated properly. However, if left untreated, it can be serious, leading to.
These clots typically begin in the. Join leading researchers in the field and publish with hindawi. A pulmonary embolism may dissolve on its own;
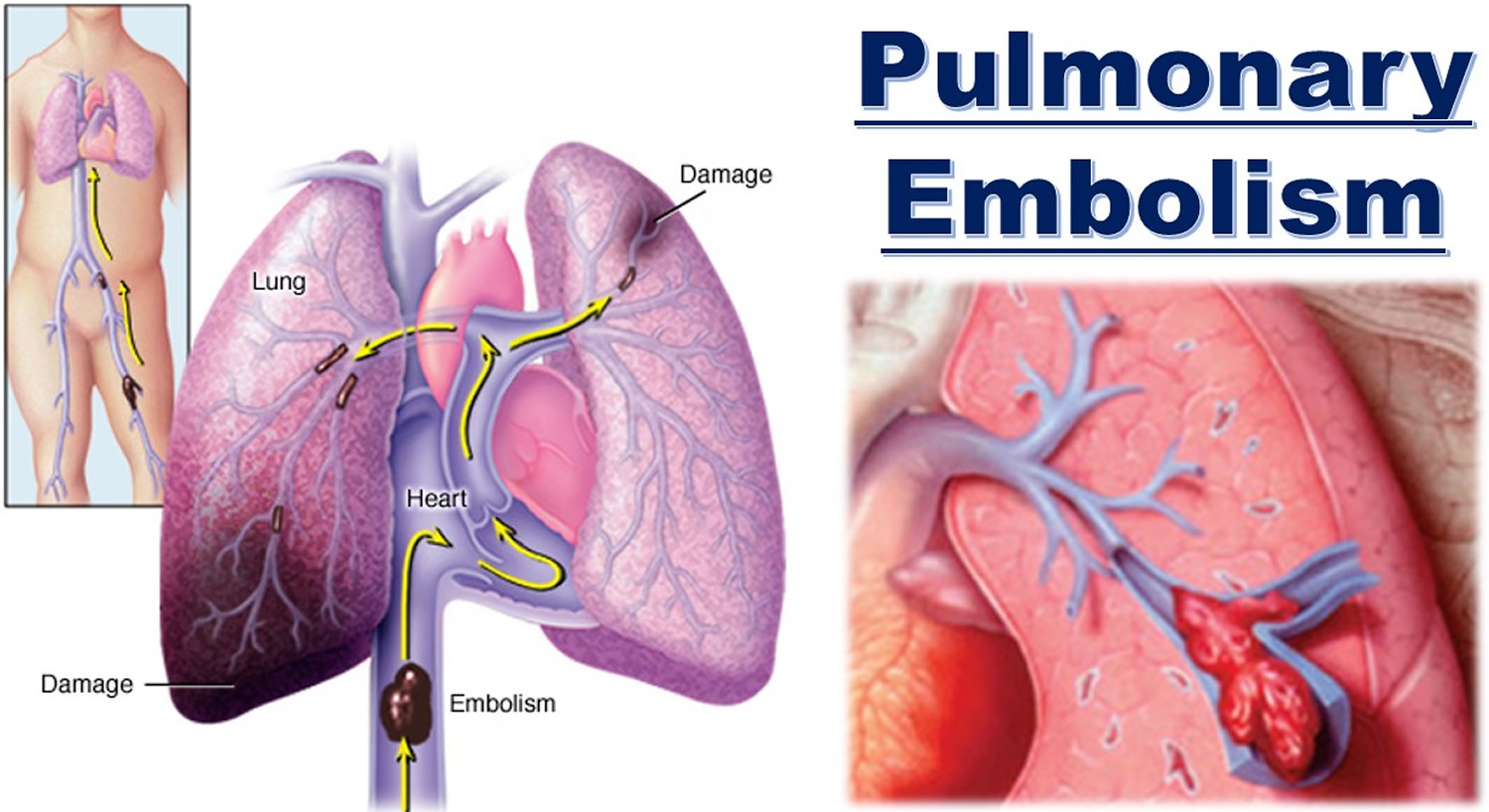
Pulmonary embolism (pe) is the presence of a blood clot (embolus) that blocks an artery in the lungs.usually the clot comes from a piece of another blood clot inside a vein of the legs (deep vein thrombosis [dvt]) that has broken off and traveled to the lungs.pulmonary emboli can range from very small and causing no symptoms to very large and causing symptoms of. Anticoagulants stop blood clots getting bigger and prevent new clots forming. It also reduces the risk of further clots developing.
A pulmonary embolism (pe) is when a blood clot becomes stuck in the blood vessels of your lung. This is a drug that causes chemical changes in your blood to stop it clotting easily. Guidelines have delineated how best to diagnose and manage patients with pe.
The medical management of pulmonary embolism consists of anticoagulation and thrombolysis. After leaving the hospital, you may need to take medicine at home for 6 months or longer. At hospital, you�ll probably be given an injection of anticoagulant medicine before you get any test results.
Blood thinners or anticoagulants for treating pulmonary embolism (pe) avoid new clots from developing while your body tries to rupture up the blood clots. The most commonly prescribed blood thinners are warfarin ( coumadin, jantoven) and heparin. All patients with pe should be treated with anticoagulation for at least 3 months [see venous thromboembolism:
This drug will stop the clot getting larger while your body slowly absorbs it. Depending on the size of the thrombus, and the location within the pulmonary arterial tree, this blockage will result in a minor decrease in oxygenation of the. Join leading researchers in the field and publish with hindawi.
This helps stop a clot from getting bigger and keep new clots from forming. Low molecular weight (lmw) heparin, such as lovenox or fragmin, which are purified derivatives of heparin that can be given by skin injection instead of intravenously. The accurate incidence of the condition is unknown, but it is estimated that 200,000 to 500,000
They’re known as “ blood thinners ” because they make it harder for your blood to clot. Pulmonary embolism (pe) usually is treated in a hospital. If a gp thinks you�ve got a pulmonary embolism, you�ll be sent to hospital for further tests and treatment.
Prompt treatment is essential to prevent serious complications or death. Warfarin is a pill and can treat and prevent clots. How pulmonary embolism is treated.
A pulmonary embolism (pe) is a blood clot in the lung that has dislodged from a vein and travels through the bloodsream.