
The guidelines recommend an intake of less than 7% of daily calories from saturated fat and less than 200 mg of dietary cholesterol. However, recommendations are less definitive for other groups such as patients with borderline.
These recommendations advocated priority to randomized.
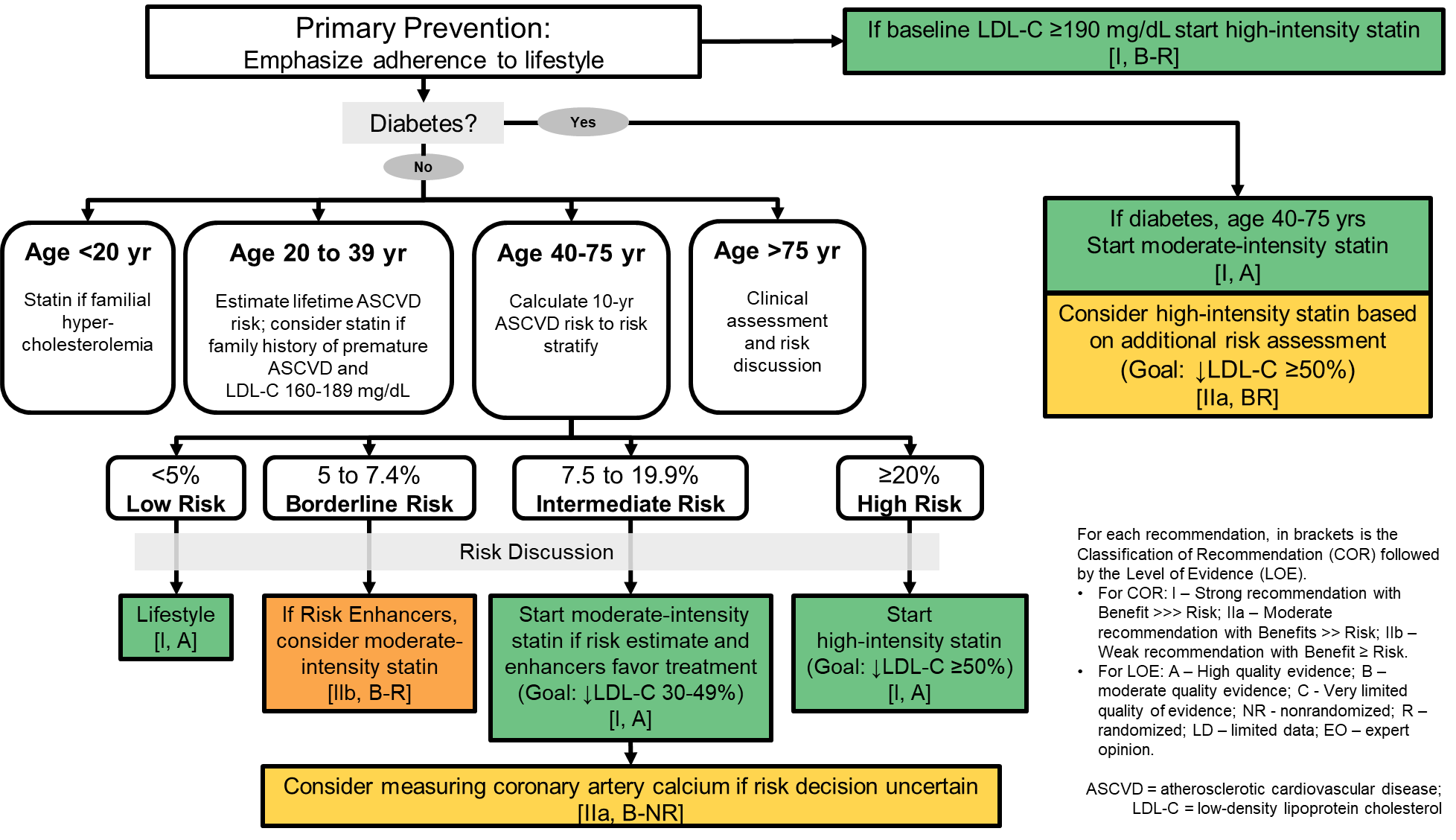
High cholesterol treatment guidelines. Emphasizing the need for nutrition, exercise, and weight control in treating high cholesterol: In type 1 patients, consider statin treatment if over 40 years or with known diabetes This was the first major update of the ncep guidelines since 1993.
The publication of cholesterol treatment guidelines by the american college of cardiology and the american heart association (acc/aha) 1 immediately met with considerable support as well some criticism related to their applicability in practice. Hyperlipidemia treatment guidelines may inform care, but cholesterol management should be tailored to the individual. Notably, target cholesterol levels have been returned to the guidelines for people in specific circumstances, to be achieved through medications and lifestyle changes.
An executive summary of the third report of the ncep expert panel on detection, evaluation and treatment of high blood cholesterol in Up to 35% of daily calories can come from total fat, provided that most of these calories are from unsaturated fats that do not raise cholesterol levels. Saturated fats are found in fatty cuts of meat and dairy products.
Individuals diagnosed with high cholesterol should try to get 40 minutes of aerobic exercise three to four times a week. The guidelines were released nov. The way you choose to lower your risk will depend on how high your risk for heart attack and stroke is.
Treatment effects of reducing cholesterol 6: Unfortunately, direct experimental evidence is extremely limited, particularly in the very old age strata of the population; The goal is not to lower your cholesterol numbers alone.
The guidelines recommend an intake of less than 7% of daily calories from saturated fat and less than 200 mg of dietary cholesterol. The american heart association recommends limiting saturated fat to less than 6% of daily calories and minimizing the amount of trans fat you eat. Then in 2013 the nhlbi guidelines for high blood cholesterol were modified to fit the criteria for guideline development required by aha/acc.
The goal is not to lower your cholesterol numbers alone. The following guidelines are from the canadian cardiovascular society (ccs).footnote 1 the two types of treatment are: In primary prevention, statins are recommended for patients with severe hypercholesterolemia and in adults 40 to 75 years of age either with diabetes mellitus or at higher ascvd risk.
The goal in treating cholesterol is to lower your chance of having a heart attack or a stroke. Eating a lot of foods high insaturated fats or trans fats,which increase “bad” ldl cholesterol. 10 at aha 2018 in chicago, il, and simultaneously published in the journal of the american college of cardiology and circulation.
The 2018 guideline covers risk assessment, primary and secondary prevention of ascvd, lifestyle New clinical practice guidelines on the prevention and treatment of high cholesterol levels in adults. Nhsl guideline for the management of cholesterol in adults treatment flow chart for patients at very high risk referred to lipid clinic.
From a dietary standpoint, the best way to lower your cholesterol is reduce your intake of saturated fat and trans fat. However, recommendations are less definitive for other groups such as patients with borderline. The following guidelines are from the american college of cardiology and the american heart association.
See section on ‘statin intolerance’ if this is an issue with atorvastatin. Access the clinical practice guideline for treatment of cholesterol endorsed with qualifications by the aafp. Hdl and ldl treatment strategies in atherosclerosis armyda atorvastatin for reduction of myocardial damage during angioplasty assign cv risk estimation model from the scottish intercollegiate guidelines network aurora a study to evaluate the use of rosuvastatin in subjects on regular haemodialysis.
Consider increasing the statin dose if these targets are not met. The criticism was based primarily on 2 issues: The two types of treatment are:
No more than 10% of your daily calories should come from saturated fats. These recommendations advocated priority to randomized. [these patients will be monitored and managed by the lipid clinic staff.] while sign 149 has no defined cholesterol level targets but aims for a.
High cholesterol treatment is not one size fits all, and this guideline strongly establishes the importance of personalized care, said acc president c. The cholesterol guidelines from the american college of cardiology and american heart association have been updated for the first time since 2013.