Although called blood thinners, these medications do. The goals of treatment for dvt are to stop clot propagation and prevent clot recurrence, pe, and pulmonary hypertension (a potential complication of multiple recurrent pes).

Venous thromboembolism (vte), which includes deep venous thrombosis (dvt) and pulmonary embolism (pe), continues to be a major cause of morbidity and mortality among hospitalized patients.
Dvt and pe treatment. Treatment was associated with the type of radiology report impression/conclusion, which were highly variable. Treatment of deep vein thrombosis (dvt), pulmonary embolism (pe), and reduction in the risk of recurrence of dvt and of pe: The 2016 chest guidelines suggest treatment of dvt of the leg and pe, in the absence of cancer, with a doac over warfarin therapy (grade 2b) based on the
Deep venous thrombosis (dvt) and pulmonary embolism (pe). These drugs don�t break up existing blood clots, but. Indications eliquis is indicated for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis (dvt), which may lead to pulmonary embolism (pe), in patients who have undergone hip or knee.
Only two of these medications, tinzaparin and enoxaparin, have been approved for the treatment of dvt and pe. Dvt is most commonly treated with anticoagulants, also called blood thinners. Reduce your chances of another dvt.
We suggest apixaban as an alternative to lmwh/vka in the acute and short term treatment of vte in appropriately selected patients. Of stroke and blood clots in people who have atrial fibrillation (afib), a type of irregular heartbeat, not caused by a heart valve problem. Venous thromboembolism (vte) has two main manifestations:
Although called blood thinners, these medications do. Medication is used to prevent and treat dvt. The first ebg document in this series dealt with prophylaxis of vte.
Ad one stop center for thrombosis dr. For patients with unprovoked dvt or pe with a low or moderate bleeding risk, extended anticoagulation is recommended. How is a dvt or pe treated?
Dvt occurs in increased percentages of trauma patients due to the combination of increased clotting tendency and immobility. John tan, 20 years in vein care Dvt/pe treatment | eliquis® (apixaban) | safety info.
John tan, 20 years in vein care Anticoagulants (commonly referred to as “blood thinners”) are the medications most commonly used to treat dvt or pe. Treatment was not independently associated with any of the clinical risk factors (age, gender, recent surgery, malignancy, or history of dvt).
Eliquis (apixaban) is a prescription medicine used to treat blood clots. Compression stockings (also called graduated compression stockings) are sometimes recommended to prevent dvt and relieve pain and swelling. Eliquis (apixaban) is a prescription medicine used to reduce the risk.
In patients with crcl <30 ml/min, rivaroxaban exposure and pharmacodynamic effects are increased compared to patients with normal renal function. In severe cases, the clot might need to be removed surgically. You will probably take the tablets for at least 3 months.
Fondaparinux (arixtra®) is a new type of anticoagulant that has been used for the prevention of dvt and pe and has recently been approved by the fda for the treatment of. Are treated essentially the same, with a few exceptions. Goals of treatment (why treat a dvt or pe)?
[ 7, 8, 9] approval for this indication was based on studies totaling 9478 patients with dvt or pe. Eliquis is indicated for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (dvt) and pulmonary embolism (pe), and to reduce the risk of recurrent dvt and pe following initial therapy. Rivaroxaban (xarelto) is an oral factor xa inhibitor approved by the fda in november 2012 for treatment of dvt or pulmonary embolism (pe) and for reduction of the risk of recurrent dvt and pe after initial treatment.
There are limited clinical data in patients with crcl 15 to <30 ml/min. Deep vein thrombosis can cause leg pain or swelling but also can occur with no symptoms. The goals of treatment for dvt are to stop clot propagation and prevent clot recurrence, pe, and pulmonary hypertension (a potential complication of multiple recurrent pes).
Similarly, for those with a second unprovoked dvt or pe, indefinite anticoagulation is recommended. Prevent the clot from getting bigger. After dvt is diagnosed, the main treatment is tablets of an anticoagulant medicine, such as warfarin and rivaroxaban.
These might need to be worn for 2 years or more after having dvt. A blood clot in your legs can also happen if you. Treatments for dvt and pe dvt.
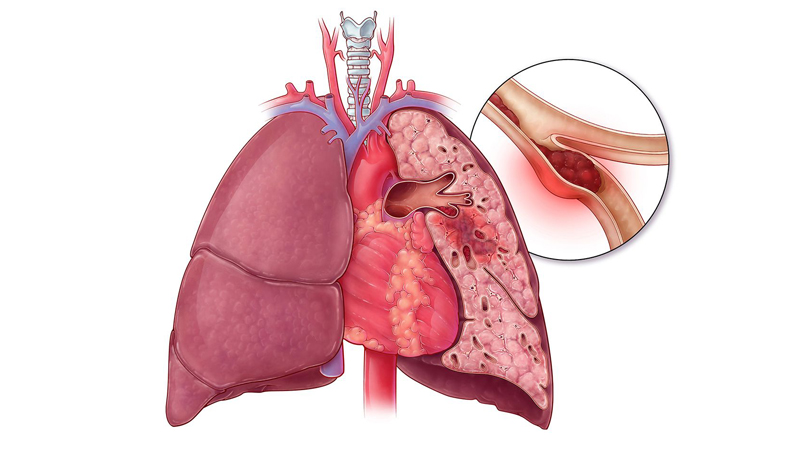
Ad one stop center for thrombosis dr. Venous thromboembolism (vte), which includes deep venous thrombosis (dvt) and pulmonary embolism (pe), continues to be a major cause of morbidity and mortality among hospitalized patients. Deep vein thrombosis (dvt) occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in your legs.
Dvt and pe can also be treated with direct oral anticoagulants (doacs). You can get dvt if you have certain medical conditions that affect how your blood clots. Prevent the clot from breaking loose and traveling to the lungs.
There are three main goals to dvt treatment. You may have an injection of an anticoagulant (blood thinning) medicine called heparin while you�re waiting for an ultrasound scan to tell if you have a dvt. Vte prophylaxis can prevent some,
These are a newer type of drug that eliminates the need for routine blood test for monitoring. Much like dvt, pe is treatable using anticoagulants to thin the blood and dissolve the clot.