
These have been compiled in a report and published in a sup Heart failure — managing newly diagnosed and decompensated patients in acute care — clinical guidelines, v1 principal author:
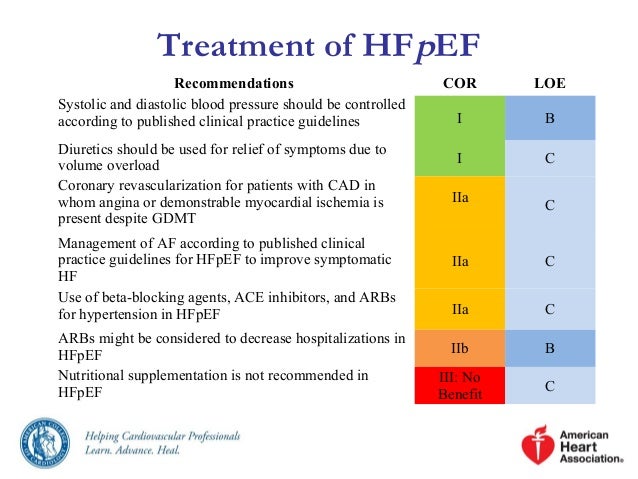
In the absence of hypertension, evidence does not support treating heart failure with preserved ejection fraction with any medication except diuretics.
Diastolic heart failure treatment guidelines. Currently, the key to the treatment of dhf is aggressive management of contributing factors. Role of 2d/3d and cmr diastolic heart function: The diagnosis of diastolic heart failure requires three conditions to be simultaneously satisfied :
The treatment of heart failure due to diastolic dysfunction has both similarities and dissimilarities to the treatment of heart failure due to systolic dysfunction. Recommendation for 1500 mg/d is applicable for stage a&b. Our recommendations do not include therapy for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy because the pathophysiologic features and therapy for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy differ significantly.
Since usual intake > 4 g/d, suggest < 3 g/d in hf for symptom. Due to association between sodium intake and htn, lvh, and cvd, the aha. Applying the new guidelines case studies william a.
2), presence of normal or only slightly reduced lv ejection fraction (ef. Guidelines for heart failure management and treatment. Normal is 50% or higher.
In the absence of hypertension, evidence does not support treating heart failure with preserved ejection fraction with any medication except diuretics. These have been compiled in a report and published in a sup Diastolic heart failure is associated with a mortality risk four times that of controls without heart failure.
Diastolic heart failure accounts for approximately one third of all heart failure cases, especially in an elderly population, and its natural Three obligatory conditions to be simultaneously satisfied for the diagnosis of dhf have been established by the european working group in 1998: Two or more admissions for treatment of decompensated heart failure within the last 12 months.
Prevention of diastolic heart failure can be achieved through better control of hypertension and other cardiovascular risk factors in the community A) with asymptomatic lv systolic dysfunction (lvef ≤30%) of ischaemic origin, who are at least 40 days after acute. Fraction / diastolic dysfunction (ef heart failure:
Bringing elevated blood pressure down to normal levels can help to prevent diastolic dysfunction from progressing to heart failure. The condition exists and needs to be recognised, prevented, and treated diastolic heart failure refers to the clinical syndrome of heart failure with a preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (0.50 or more) in the absence of major valve disease.1 about a third of patients with heart failure seen by clinicians have diastolic heart failure as defined above.2 a simple. The understanding of the phenotypic heterogeneity and multifactorial pathophysiology of dhf may lead to novel therapeutic targets in the future.
Updating of these guidelines will be. Download a free heart failure treatment guide from cleveland clinic, home of the nation’s top cardiology and cardiac surgery program. Zoghbi md, fase, macc professor and chairman, department of cardiology elkins family distinguished chair in cardiac health houston methodist hospital relation with industry •none relevant
Presence of normal or mildly abnormal lv systolic function; Esc guidelines are more descriptive in. Presence of signs or symptoms of congestive heart failure;
All experts involved in the development of these guidelines have submitted declarations of interest. Diastolic heart failure •also referred to as “hf with preserved ejection fraction” (hfpef) •clinical diagnosis of heart failure + lvef greater than or equal to 50% •commonly due to hypertension •patients often are older and female •high prevalence of obesity, diabetes, atrial fibrillation Treatment of diastolic hf is aimed to stop the progression of the disease, relieve its symptoms, eliminate exacerbations and reduce the mortality.
1), presence of signs and symptoms of heart failure; Heart failure — managing newly diagnosed and decompensated patients in acute care — clinical guidelines, v1 principal author: Introduction — heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (hfpef) is a clinical syndrome in which patients have symptoms and signs of hf as the result of high ventricular filling pressure despite normal or near normal left ventricular ejection fraction (lvef ≥50 percent) [].most patients with hfpef also display normal lv volumes and evidence of diastolic.
Current treatment of diastolic heart failure is empirical. The nottinghamshire heart failure lights denote the colours green, amber and red which indicates the clinical/therapeutic and service classification of patients’/carers journey along and between an integrated care pathway for heart failure and recommendations for treating heart failure (nice 2018). The management should include antihypertensive treatment, maintenance of the sinus rhythm, prevention of tachycardia, venous pressure reduction, prevention of myocardial ischemia and prevention of diabetes mellitus.
Evidence of diastolic lv dysfunction. The american heart association (1) and european society of cardiology (2) are broadly in agreement with their definitions of hfpef as representing patients with signs and symptoms of heart failure, evidence of normal or preserved ejection fraction but objective evidence of other structural or functional alterations in cardiac structure; Check here for latest testing information, visitor restrictions + service changes.
This is measured by ejection fraction (ef) or the percentage of blood that is ejected out of the ventricle.