Return to algorithm return to table of contents. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 dibetes, 2018.
Nice guideline 28—type 2 diabetes in adults:
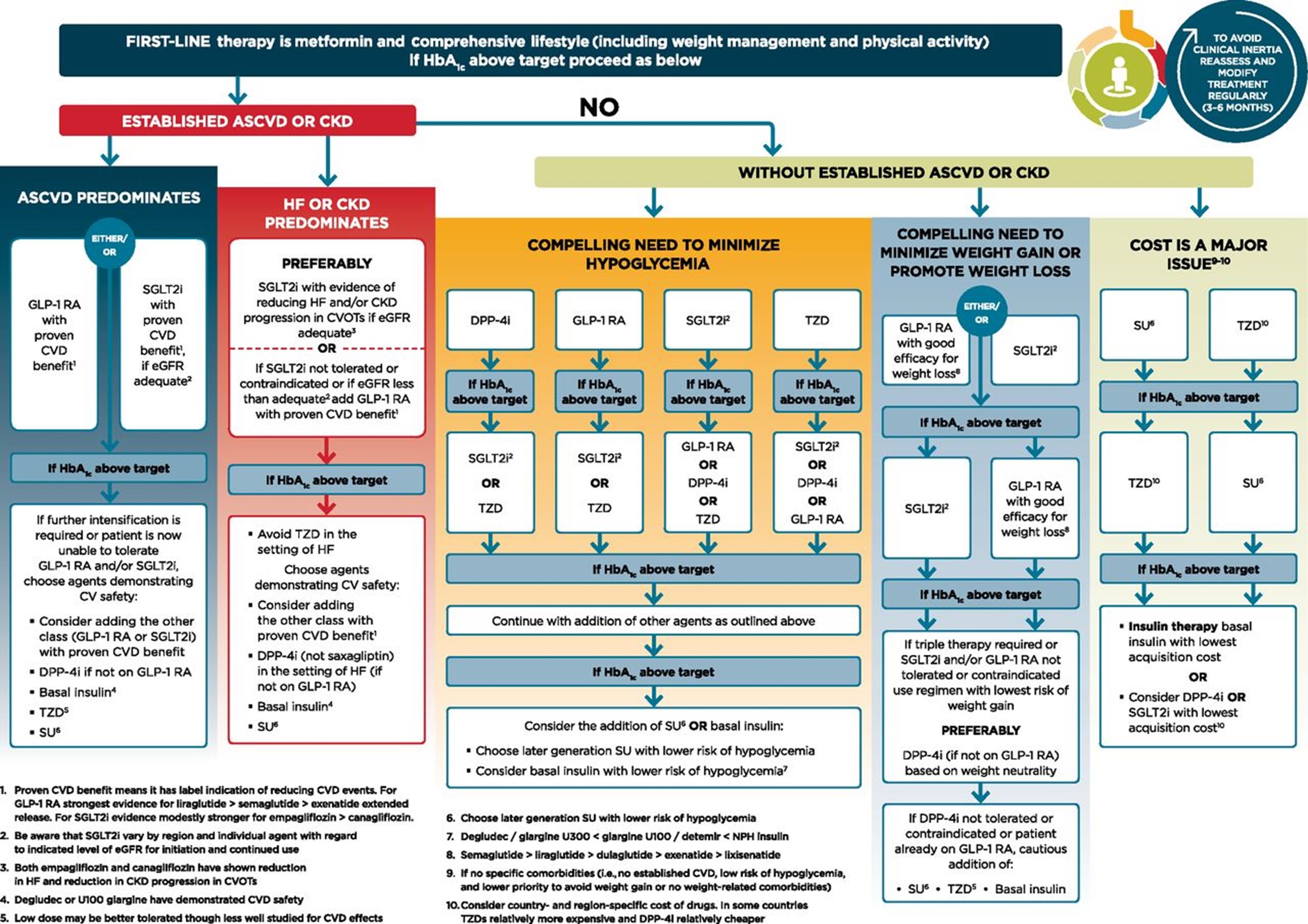
Diabetes type 2 treatment guidelines. Goals should be individualized based on duration of diabetes, age/life expectancy, comorbid conditions, known cvd or advanced microvascular complications, hypoglycemia unawareness, and individual Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 dibetes, 2018. Metformin is the preferred initial pharmacologic agent for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Return to algorithm return to table of contents. Although the place of metformin as first line in the treatment of type 2 diabetes is well established, it is important to note that the only cv outcome trial to support its beneficial cv effect was the ukpds trial , where only 342 patients were included in the metformin arm and the number of coronary death events was 16 with metformin compared with 36 in the competing. 500 mg once daily in the morning at breakfast week 2:
Fasting plasma glucose (mg/dl) <90 1 hour postprandial glucose (mg/dl). Individualize all glycemic targets (a1c, fpg, ppg) 5. Besides glycemic control, fetal growth and maternal blood pressure need to be monitored.
The aim of treatment is to reduce hba1c to agreed target levels in order to reduce long term complications from diabetes. A nonsensus report by the american diabetes association (ada) and the european association for the study of diabetes; (2) to avoid side effects of treatment, especially the most associated with impaired quality of life such as hypoglycaemia and falls;
In individuals at risk for type 2 diabetes (see table 1), type 2 diabetes can be delayed or prevented through diet, exercise, and pharmacologic interventions. Possibly, diabetes medication or insulin therapy; Once initiated, metformin should be continued as long as it is tolerated and not contraindicated;
And (3) to have a global vision of the patient, introducing. 76 while the guidelines of pharmacologic treatment for type 2 diabetes in the united. Strategies for the prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes;
Sign guideline 154—pharmacological management of glycaemic control in people with type 2. 0.25 mg sc weekly x 4 wks. Once type 2 diabetes is established it is recommended that blood glucose lowering agents are used by all international guidelines.
0.6 mg sc daily x 7 days then titrate 1.2 mg sc daily (a lower starting dose of 0.3 mg with a slower titration schedule can be considered if gi intolerance is a concern) (3) semaglutide (ozempic): Diabetes care ada guidelines january 2020. Based on all the above, the treatment of diabetes in the elderly people should achieve the following objectives:
Icmr guidelines for management of type 2 diabetes 2018 65. The guidance is designed as a concise pragmatic resource for all health professionals working with people with type 2 diabetes in new zealand and will be updated as. Clinicians should perform regular screening for prediabetes and diabetes in the older population and implement interventions as indicated in this guideline.
Learning about these drugs — how they�re taken, what they do and what side effects they may cause — will help you discuss treatment options with your doctor. Individualized treatment * more or less stringent glycemic goals may be appropriate for individual patients. And therapeutic approaches that can reduce complications, mitigate.
This type of diabetes is largely the result of excess body weight and physical inactivity. The list of medications for type 2 diabetes is long and potentially confusing. Type 2 diabetes management algorithm 1.
The current nice guideline, ng28, which was published in 2015 includes an algorithm for. Lifestyle modification underlies all therapy (e.g., weight control, physical activity, sleep, etc.) 2. Other agents, including insulin, should be added to metformin.
Then titrate 0.5 mg sc weekly (4)dulaglutide (trulicity): Post op, metformin will likely be continued and other This guideline covers care and management for adults (aged 18 and over) with type 2 diabetes.
1 g morning and evening) 3. See the nice guidance on canagliflozin in combination therapy for treating type 2 diabetes, dapagliflozin in combination therapy for treating type 2 diabetes and empagliflozin in combination therapy for treating type 2 diabetes. More than 95% of people with diabetes have type 2 diabetes.
500 mg 2 times daily (morning and evening) during meals increase in increments of 500 mg per week as long as the drug is well tolerated (max. These steps will help keep your blood sugar level closer to normal, which can delay or prevent complications. The prevalence of type 2 diabetes increases as individuals age and exaggerates the incidence of both microvascular and macrovascular complications.
In december 2020, we made minor changes to the recommendations on diabetic retinopathy to. Optimal a1c is ≤6.5%, or as close to normal as is safe and achievable 6. Therefore, in initiating subcutaneous insulin in a hospitalized patient who is eating meals, a total daily insulin dose of 0.6 units/kg is probably reasonable (clement, 2004).
Management of type 2 diabetes includes: (1) to avoid disability, ensuring the best quality of life; Treatment with combinations of medicines including sglt2 inhibitors may be appropriate for some people with type 2 diabetes;
Contrary to popular perception, there�s no specific diabetes diet. Nice guideline 28—type 2 diabetes in adults: The usual dose is 1 to 2 g daily.
