Addition of clavulanic acid offers a broader spectrum; The nhs protocol for management of copd exacerbations in primary care states that bronchodilators and corticosteroids are the mainstay of exacerbation treatment.
Treatment of acute exacerbations involves.
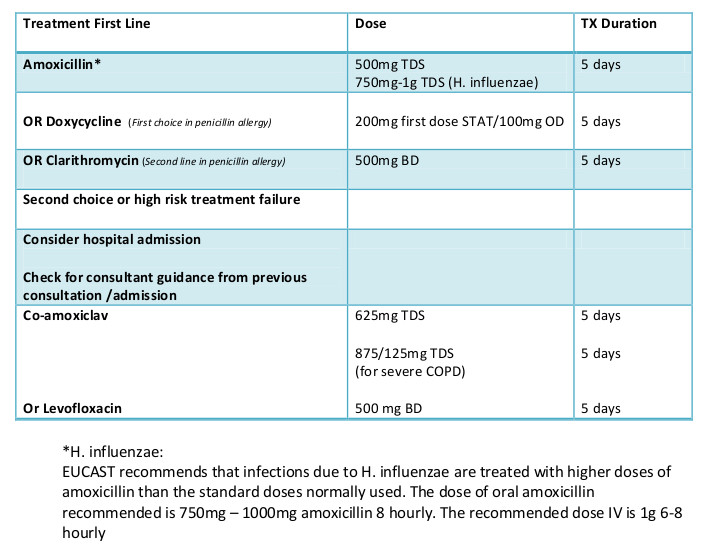
Copd acute exacerbation treatment. Classification is via gold’s classification (see diagnosis and management of stable copd in ‘related topics’ below). For antibiotic treatment of acute exacerbations of copd (aecopd) the national guidelines in denmark recommend either first choice amoxicillin 750 mg tid (amx) or amoxicillin with clavulanic acid 500 mg/125 mg tid (amc). Can be used to guide treatment steps.
Addition of clavulanic acid offers a broader spectrum; Copd characterized by the cardinal symptoms of dyspnea, cough, increased sputum purulence and production/volume. Care of the hospitalized patient with acute exacerbation of copd patient population:
‘an acute and sustained worsening of symptoms that require additional treatment’2 •treated with systemic corticosteroids and antibiotics (unselectively) 1. Six studies including 670 participants contributed data on mortality. A university veterans affairs medical center.
•over 1.5 million gp consultations annually in uk related to exacerbation1 definition: The quality of evidence was low. The evidence was appraised using the grading of
The routine administration of oxygen at high concentrations during a copd exacerbation has been associated with a higher mortality rate than with a titrated oxygen approach. Procedure or treatment must be made by the physician in light of the circumstances presented by the patient. Sometimes ventilatory assistance with noninvasive ventilation or intubation and ventilation.
A randomized, controlled multicentric study of inhaled budesonide and intravenous methylprednisolone in the treatment on acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Meta‐analysis showed no statistically significant effects of rehabilitation on mortality (pooled or 0.68, 95% ci 0.28 to 1.67). The nhs protocol for management of copd exacerbations in primary care states that bronchodilators and corticosteroids are the mainstay of exacerbation treatment.
Opposite, amx alone in a higher dose may offer more time above mic. Treatment of pneumonic aecopd consists of treating both pneumonia and copd. A retrospective chart analysis over 24 months.
Treatment of acute exacerbations involves. The study found that home‐based telehealth hospitalization was noninferior to conventional hospitalization when the noninferiority margin was set at 20% of the control group�s risk of readmission.109 the data suggest that a subgroup of patients with severe copd may be treated for acute exacerbation at home using telehealth, without the physical presence of. Abstract this document provides clinical recommendations for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) exacerbations.
One potential approach to a patient with copd and possible pneumonia is the following: Explain recent evidence supporting a shorter duration of steroid treatment for acute exacerbations of copd. Give oral antibiotics first line if the person can take oral medicines, and the severity of their exacerbation does not require intravenous antibiotics.
Review intravenous antibiotics by 48 hours and consider stepping down to oral. In chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, a combination of ipratropium and albuterol is more effective than either agent alone. Treatment of chronic stable copd aims to prevent exacerbations.
Identify which patients with an acute exacerbation of copd should receive antibiotics. Firm diagnosis of copd and helps stage copd severity. Older, frail patients and patients with comorbidities, a history of respiratory failure, or acute changes in blood gas measurements are admitted.
Procalcitonin (pct) may be helpful in determining if antibiotics are necessary or the duration of treatment. When prescribing an antibiotic for an acute exacerbation of copd, follow table 1 for adults aged 18 years and over. Discuss the initial treatment of acute exacerbations of copd.
Acute exacerbation of copd typically presents with an increased level of dyspnoea, worsening of chronic cough, and/or an increase in the volume and/or purulence of the sputum produced.may represent the first presentation of copd, usually associated with a history of tobacco exposure.treatment includ To determine the effect of age, severity of lung disease, severity and frequency of exacerbation, steroid use, choice of an antibiotic, and the presence of comorbidity on the outcome of treatment for an acute exacerbation of copd. 7 however, a systematic review of 19 copd guidelines reported that the criteria for treating patients with antibiotics were largely based on an increase in respiratory symptoms, while.
Acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd) are treated with oxygen (in hypoxemic patients), inhaled beta 2. Mild exacerbations often can be treated on an outpatient basis in patients with adequate home support. (1) start on antibiotic coverage for pneumonia (e.g.
Effects of combined treatment with glycopyrrolate and albuterol in acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The goal of therapy when treating a copd exacerbation is to minimize the negative impact of the current exacerbation and prevent future events. A person with copd can experience a period when their symptoms are much worse than usual.
Exacerbations involve increased airway inflammation, increased mucus production and increased gas trapping. This is known as an acute exacerbation.
