Technological advancements permit the collection and merging of large heterogeneous datasets from different sources, from genome sequences to social media posts or from electronic. Nowadays, trendy research in biomedical sciences juxtaposes the term ‘precision’ to medicine and public health with companion words like big data, data science, and deep learning.
However, the key enabler of precision medicine is the dramatic decrease in genome sequencing costs.
Big data precision medicine. This is the power of precision health. From big data to precision medicine access to data, which are provided willingly by the customer and delivered directly and centrally to the company. Precision medicine is gaining ground with the advancement of such technologies as ai, mobile healthcare, and big data analytics that largely supports precision medicine.
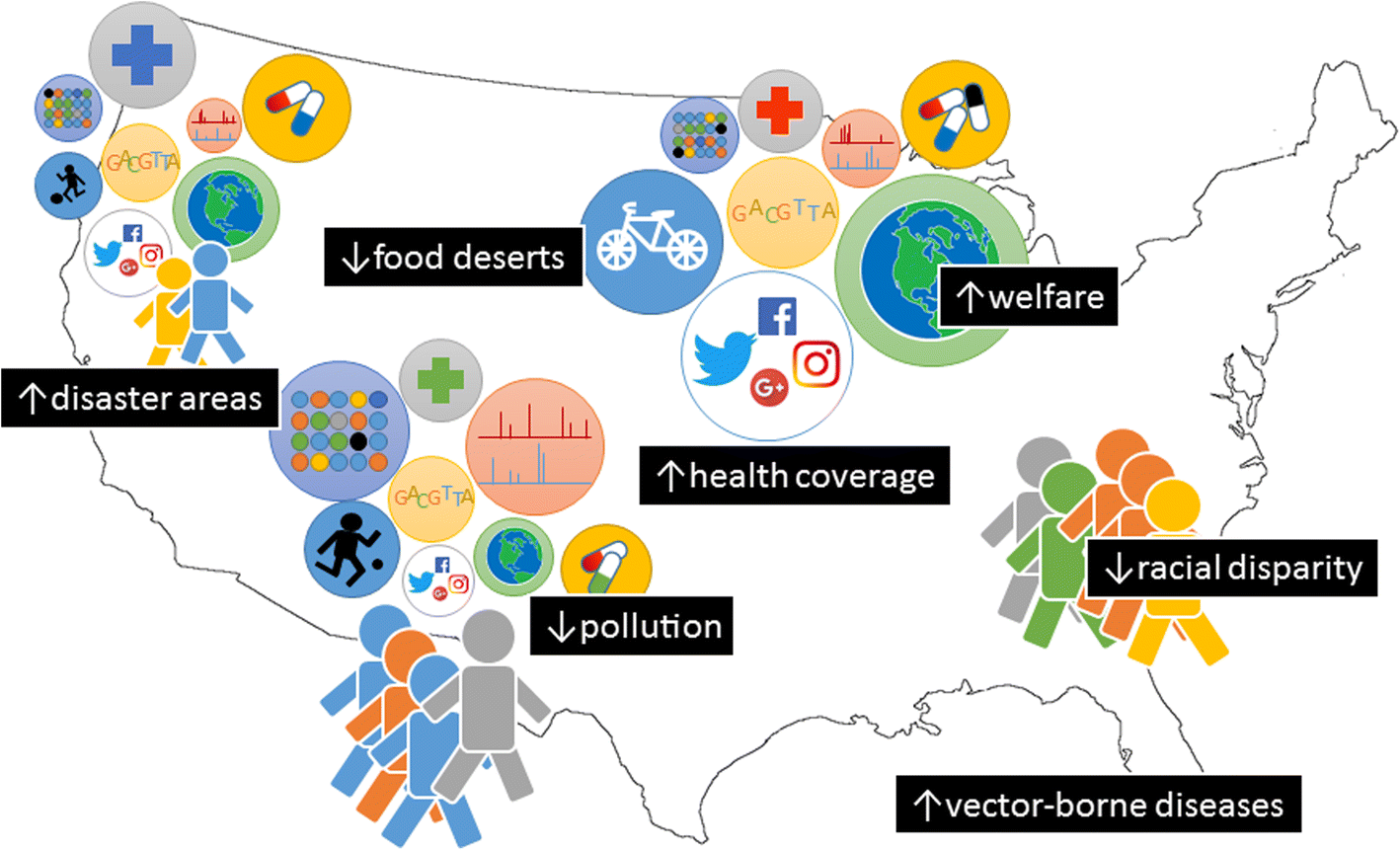
The rapid development of precision medicine is driven by the development of omics related technology, biological information and big data science. Technological advancements permit the collection and merging of large heterogeneous datasets from different sources, from genome sequences to social media posts or from electronic. Is it possible that large volume medical information from individual patient data
However, the key enabler of precision medicine is the dramatic decrease in genome sequencing costs. According to the market research, the precision medicine software market is expected to grow from $1.2 billion to approximately $2 billion by 2024. Nowadays, trendy research in biomedical sciences juxtaposes the term ‘precision’ to medicine and public health with companion words like big data, data science, and deep learning.
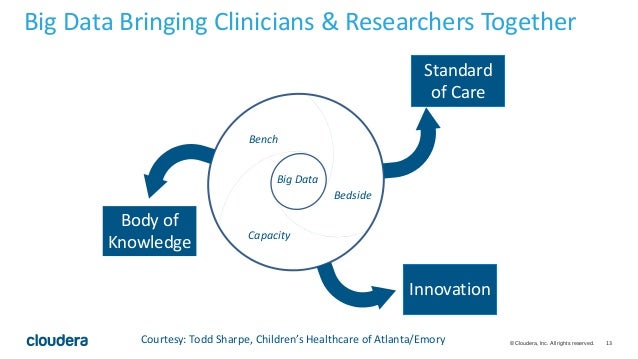
Big data for precision medicine. Big data analytics covers integration of heterogeneous data, data quality control, analysis, modeling, interpretation and validation [ 5 ]. There cannot be exceptionalism for ai in medicine.
Healthcare organizations deal with gigantic amount of patient data and ai algorithms can be employed to scrutinize this data to. Rothstein, mark a., big data, surveillance capitalism, and precision medicine. Yet the human ability to process this data without effective decision support is finite.
Suggested citation hopp, wallace j. Big data and precision medicine in cancer: Big data becomes crucial for processing the enormous amount of diverse information that precision medicine requires.
On the one hand, the goal of precision medicine is to harness that data to benefit patients by better tailoring treatments and preventative care. Big data, precision medicine, observational data, machine learning, causal inference suggested citation: From big data to precision medicine.
The big data market is expected to reach over $123 billion by 2025! Challenges to face esther paniagua. Including health information increasingly used in precision medicine research, present great challenges for health privacy.
21 february 2019 cancerworld plus 0. Precision medicine is treated developing the key point that high From big data to precision medicine front med (lausanne).
By using big data tools, the information can be analyzed computationally to discover insights for customizing medical treatments and preventions. A great challenge regarding the big data in healthcare, bioinformatics and precision medicine is the extraction of insightful, actionable knowledge from the streams of omics data related to patients that can be translated into effective therapies tailored to the molecular characteristics of the actual, biological state of an individual. Karnes 4, orsolya varga 5, stine hedensted 6, roberto spreafico 7, david a.
Precision medicine is provided to implement precise and personalized treatment for diseases and specific patients. While ai and big data are more and more used to tackle cancer, experts caution: Precision medicine is a new therapeutic concept and method emerging in recent years.
“doing the right thing, in the right way, at the right time, in the right place, to the right person, for the right reason, with the right feeling.the first time.” 12. The big data revolution is making vast amounts of information available in all sectors of the economy including health care. In part 1 big data collected for research purposes (big research data) and big data used for research although collected for other primary purposes (big secondary data) are discussed in the light of the fundamental common requirement of data validity, prevailing over bigness.
One important type of data that is particularly relevant to medicine is observational data from actual practice. Big data for precision medicine. Hafler 8 and eoin f.
And li, jun and wang, guihua, big data and the precision medicine revolution (april 17, 2018). It identifies the patterns, trends, and associations of those large data sets. Big data in healthcare and medicine refers to these various large and complex data, which they are difficult to analyse and manage with traditional software or hardware ,.
“click through” consent online, compelled authorizations, and the development of algorithms that generate associations from diverse. A world in which we can prevent disease before it strikes and cure it decisively if it does. Tim hulsen 1 *, saumya s.
Personalized medicine or precision medicine will be implemented after analyzing patient’s health history, genetic data, preferences, and environmental exposure for diagnosis of illness or for further treatment. But it also raises ethical issues relating to the balancing of interests, viability of anonymization, familial and group implications, as well as genetic discrimination. To predict, prevent, and cure disease — precisely.
Precision health is a fundamental shift to more proactive and personalized health. Building on progress in pharmacogenetics, pharmacogenomics and targeted therapy, precision medicine (pm) aims at integrating multiple data sources to ‘tailor medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient’ (national research council, 2011).the development of precision medicine is therefore premised on the collection of large.