
Mary mcmahon a patient�s age can determine appropriate treatment for aspiration pneumonia. Ats and idsa agreed on moving from the narrative style of previous documents to the grading of recommendations assessment, development, and evaluation (grade) format.
{{configctrl2.info.metadescription}} this site uses cookies.
Aspiration pneumonia treatment guidelines. Treatment of aspiration pneumonitis is primarily supportive. Guideline 133fm.17.1 6 of 13 uncontrolled if printed 3. Oral hygeine and regular dentistry care are important to reduce risk for aspiration pneumonia in neurologically impaired patients.
In contrast to chemical pneumonitis, antibiotics are the most important component in the treatment of aspiration pneumonia. In patients who are not intubated, humidified oxygen is administered, and the head end of the bed should be raised by 45 degrees. Iv amoxicillin 1g 8 hourly + metronidazole 500mg 8 hourly.
No randomized, controlled trials have shown a role for glucocorticoids in the routine treatment of aspiration pneumonia, and we do not recommend their use. These factors included debilitation, impaired consciousness (including general anesthesia), esophageal and neurologic disorders, cardiac resuscitation, and the presence of a nasogastric tube or tracheostomy. In patients with primary or secondary bacterial aspiration pneumonia (not chemical pneumonitis), the following recommendations may be considered:
The treatment varies between aspiration pneumonia and aspiration pneumonitis. The patient�s position should be adjusted, followed by the suction of oropharyngeal contents with the placement of the nasogastric tube. Sputum culture and gram stain are usually inconclusive but may identify the infecting organism.
Ats and idsa agreed on moving from the narrative style of previous documents to the grading of recommendations assessment, development, and evaluation (grade) format. A multidisciplinary panel conducted pragmatic systematic reviews of the relevant research and applied grading of recommendations, assessment, development, and evaluation. As with most great questions, there is no clear answer to the optimal antibiotic regimen for aspiration pneumonia.
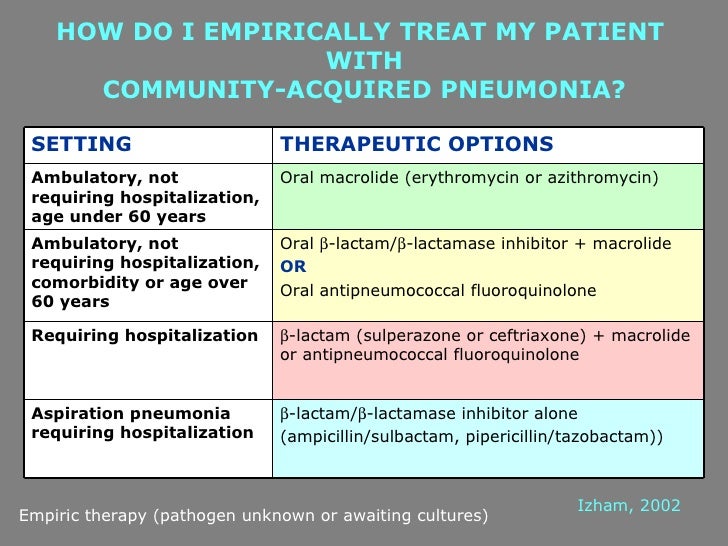
We recommend not routinely using corticosteroids in nonsevere cap. Treatment for aspiration pneumonia can include medications to kill infectious organisms in the lungs, breathing support, and rest to help the patient recover. Aspiration pneumonia do not give antibiotics automatically for acute aspiration event, as this may be chemical pneumonitis send sputum for culture stop if no evidence of consolidation on cxr first line treatment second line treatment or type 1 penicillin
Many aspects of the management of cap are not covered in this document, including items By continuing to browse this site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Practice guidelines for preoperative fasting and the use of pharmacologic agents to reduce the risk of pulmonary aspiration:
Prevention is the overall theme here—immediate orotracheal suctioning, oxygenation strategies, and handoff reporting procedures are all important aspects to review when looking at ems aspiration. Aspiration pneumonitis and aspiration pneumonia. Several factors can play a role in treatment recommendations including the patient’s age and overall level of health, along with.
{{configctrl2.info.metadescription}} this site uses cookies. Aspiration pneumonia occurs most commonly in patients with a predisposition to aspiration (eg, those with neurological bulbar dysfunction). Secondary prevention of aspiration using various measures is a key component of care for affected patients.
To study the factors associated with aspiration pneumonia, 88 cases of aspiration have been reviewed. The risks of anaerobic infection in aspiration pneumonia are largely overstated. Mary mcmahon a patient�s age can determine appropriate treatment for aspiration pneumonia.
(m) we suggest no routine use in influenza pna. Treatment comprised administration of oxygen,. Uncomplicated pneumonia treatment in the outpatient setting usually should last 5 to 10 days.54 inpatient admission for pneumonia warrants longer duration of antibiotic therapy, typically 7 to 10 days of combined parenteral and oral therapy or at least 1 week after becoming afebrile.58 complicated cases of pneumonia will require a minimum of 2 weeks of therapy.
Infection usually involves the dependent lung lobe. Application to healthy patients undergoing elective procedures: The treatment recommendations highlighted in this document are not meant to be a comprehensive guideline, but do reflect therapeutic recommendations in the 2019 ats/idsa cap guidelines.
Waiting for the results of culture is unwise and will disappoint because of the low yield. An updated report by the american society of anesthesiologists task force on preoperative fasting and the use of pharmacologic agents to reduce the risk of pulmonary aspiration. The debate on aspiration pneumonia treatment guidelines.
There is limited evidence regarding the involvement of anaerobes in most cases of aspiration pneumonia. Early empirical treatment is required for cases that are severe enough to warrant hospitalisation. Ciprofloxacin 500 mg po bid or 400 mg iv bid
Aspiration pneumonia should be treated with antibiotics; Updated recommendations from the ats and idsa [practice guidelines] (h) we suggest no routine use in severe cap.
Oral amoxicillin 1g 8 hourly + metronidazole 400mg 8 hourly. Review intravenous antibiotics by 48 hours and consider switching to enteral route if possible. Aspiration pneumonia is diagnosed based on clinical signs or symptoms of pneumonia in a person with a history of, or risk factors for, aspiration.
(l) we endorse the surviving sepsis campaign recommendations on use in cap and refractory shock. Aspiration pneumonia treatment guidelines for prehospital and ems personnel include strategies to prevent aspiration in order to improve patient care and overall clinical outcomes.