The relative efficacy of antiarrhythmic drugs (aads) after electrical cardioversion are not well established. Inadequacies in current therapies for atrial fibrillation have made new drug development crucial.
Cryoablation for afib is recommended for people for whom antiarrhythmics have been ineffective or who are unable to take antiarrhythmics due to side effects.
Antiarrhythmic medications for afib. Rate controlling medications and antiarrhythmics can be quite effective in controlling atrial fibrillation but can be associated with a variety of side effects which people may not be able to tolerate. Depending on your heart condition, you may receive medications through an iv or by mouth to help return your heart to normal rhythm. Treatment options of afib include lifestyle changes, medications, and procedures such as cardioversion or ablation.
Afib causes a higher risk of stroke and other related cardiovascular events, so one of the primary treatment goals is protecting against the formation of blood clots. It is also used to treat or prevent clots in the lungs or in the veins. Medications that are commonly associated with an increased risk of developing atrial fibrillation include dobutamine and the chemotherapy agent cisplatin.
Multaq ® is an antiarrhythmic drug indicated to reduce the risk of hospitalization for atrial fibrillation (afib) in patients in sinus rhythm with a history of paroxysmal or persistent afib. Vernakalant is one such new multichannel blocking antiarrhythmic drug. Cryoablation is also an option for people with afib who do not want to take daily medications.
What medications cause atrial fibrillation? We have antiarrhythmic medications and ablation procedures. A new study from researchers at the university of illinois at chicago is the first to show that some antiarrhythmic medications used to.
The class i agents are grouped into class ia (which depress phase 0), class ib (which have little effect on phase 0 in normal tissue), and class ic (which markedly depress phase 0). This study aimed to investigate the efficacies of different aads for maintaining sinus rhythm (sr) after electrical cardioversion for atrial fibrillation (af). The problem arises from the fact that many of.
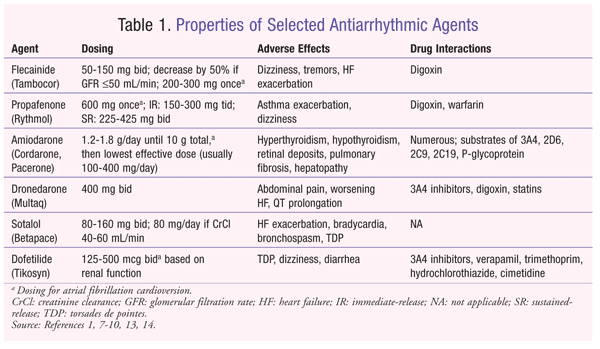
Some antiarrhythmic medications used to treat atrial fibrillation (afib) are less effective in patients who are obese, say researchers of the university of illinois at chicago. Also called tambocar and rythmol. Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormal rhythms of the heart, such as atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation.
Cryoablation for afib is recommended for people for whom antiarrhythmics have been ineffective or who are unable to take antiarrhythmics due to side effects. We selected patients from a re. Atrial fibrillation, or afib, is a type of heart disorder that can cause an abnormally high heart rate.
Atrial fibrillation medications among the medications typically prescribed to treat atrial fibrillation, the most common is the anticoagulant drug warfarin. In patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (af) undergoing pulmonary vein ablation, the use of antiarrhythmic medications in the first 6 weeks postprocedure has been shown to decrease early recurrence of atrial arrhythmias in a randomized controlled trial (the antiarrhythmics after ablation of atrial fibrillation study). Impacting the bioavailability of multaq.
Cardioversion is a treatment that sends an electric “shock” to your heart to restore a normal heartbeat. 3 class i drugs block sodium influx into the cells and therefore slow the atrial as well as ventricular conduction velocity and, it is hoped, terminate the arrhythmia. Many attempts have been made to classify antiarrhythmic agents.
These medicines are often prescribed as a “pill in the pocket” and taken at the onset of afib instead of every day. The relative efficacy of antiarrhythmic drugs (aads) after electrical cardioversion are not well established. New antiarrhythmic drugs for treatment of atrial fibrillation.
Because of the stroke risk, it is important to take medications if your doctor recommends it. During cardioversion, an abnormal heart rhythm is converted to a normal heart rhythm. The best type of treatment that is recommended for a patient is based on their symptoms.
Your first doses are given in. Apixaban (eliquis) is an expensive drug used to lower the chance of stroke in people with a medical condition called atrial fibrillation. Inadequacies in current therapies for atrial fibrillation have made new drug development crucial.
Conventional antiarrhythmic drugs increase the risk of ventricular proarrhythmia. You may need a cardioversion if your arrhythmia does not stop after taking the antiarrhythmic medication. Several drugs can be used to treat afib, such as heart rate control, anticoagulants, and antiarrhythmic medications.
Most new antiarrhythmic medications are formulated with the intent of reducing proarrhythmic toxicity. It is used to manage afib if the heart muscle pumping function is normal and the patient does not have coronary artery disease. If you need a cardioversion, your healthcare team will give you more detailed information about the procedure.
Both of these are really designed to suppress the triggers of afib,” explained dr. Several antiarrhythmic drugs are commonly used to prevent atrial fibrillation recurrence, such as quinidine, flecainide, propafenone, sotalol, and dofetilide. These medications may be used singly or in conjunction, depending on what your physician recommends.
It comes in 50mg, 100mg or 150mg.
